 |
A python package is a collection of python modules. These modules are python scripts with *.py file extension. Typically, these scripts will contain python functions, classes, custom data types etc.
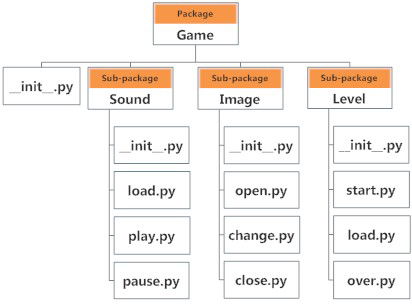
Looking at the figure above, the Game package consist of an _init_.py file together with 3 other sub-packages Sound, Image and Level respectively.
The _init_.py file must be included inside a directory for it to be considered a python package.In addition, the directory must be defined inside sys.path.
Example usage:
1. import Game.Level.Start- Suppose the start.py module consists of a function called mince()
- Inside your python application, you would need to call it as follows
- Alternatively, you can reference it as follows
3. from Game. Level import Start // recommended approach
4. Start.mince(<input_params>)
- A less common method is calling the function as if it was defined inside your current script
5. from Game.Level.Start import mince //not recommended
6. mince(<input_params>)
Comments
Post a Comment